If one is going to play any form of contact sport, it is essential to be familiar with the risks that come with participation in the sport. As rugby is about as contact-full as any sport can be, being aware of concussions is necessary and how to avoid them is critical.
A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by a blow to the head, a sudden jolt, or a violent shaking of the head and body. It’s characterized by a temporary disturbance in brain function, typically resulting from the brain hitting against the skull.
Concussions are common in contact sports like rugby, football, hockey, and others, but they can also occur due to falls, accidents, or any sudden impact to the head.
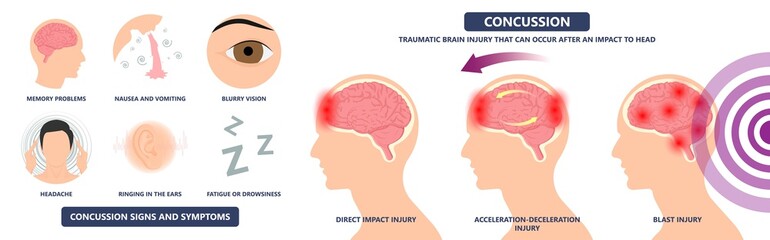
Symptoms of a concussion can vary widely and might not always be immediately apparent. Some common signs and symptoms include:
Headache or Pressure: Persistent or worsening headache is a frequent symptom.
Confusion or Disorientation: Feeling dazed, confused, or experiencing memory problems.
Nausea or Vomiting: Feeling queasy or vomiting after the injury.
Balance Problems: Dizziness or difficulty maintaining balance.
Sensitivity to Light or Noise: Sensitivity to light or sound that wasn’t present before.
Changes in Mood or Behavior: Irritability, mood swings, or changes in behavior.
Concentration or Memory Issues: Difficulty concentrating or remembering things.
Temporary Loss of Consciousness: Loss of consciousness can occur, but it doesn’t always happen with a concussion.
It’s essential to take concussions seriously as they are a form of brain injury. In many cases, symptoms may not appear immediately after the injury but could develop over hours or days.
Management of concussions involves rest, both physical and cognitive, until symptoms subside. It’s crucial to allow the brain to heal properly and avoid activities that could exacerbate symptoms.
In sports, players suspected of having a concussion should be immediately removed from play and evaluated by a healthcare professional trained in concussion management.
Seeking medical attention is essential if you suspect a concussion, especially if symptoms are severe, worsen over time, or if there’s loss of consciousness.
Returning to normal activities, including sports, should only occur after clearance from a healthcare professional specialized in concussion management to prevent the risk of further injury or complications.
Concussions are a significant concern in rugby due to the physical nature of the sport. The high-speed collisions, tackles, and physicality inherent in the game can increase the risk of head injuries, including concussions.
Rugby’s governing bodies, including World Rugby, have taken steps to address and manage concussions to prioritize player safety. Here are some key points regarding concussions in rugby:
Awareness and Education: Players, coaches, referees, and medical staff receive education and training on recognizing and managing concussions. This includes understanding symptoms, the importance of immediate removal from play if a concussion is suspected, and proper concussion protocols.
Concussion Protocols: Rugby has established strict protocols for managing concussions during matches. If a player is suspected of having a concussion, they must undergo an immediate assessment by a qualified medical professional. If diagnosed, the player is removed from the game and cannot return until cleared by a healthcare professional specialized in concussions.
Player Welfare: The welfare of players is a priority. Rugby organizations have implemented measures to ensure players receive appropriate medical care and have recovery periods that prioritize their long-term health over the immediate demands of the game.
Research and Guidelines: Ongoing research is conducted to understand the impact of concussions and to develop guidelines for safer play. This includes studying the frequency and effects of concussions in rugby and exploring ways to reduce the risk of head injuries.
Rule Changes: There have been discussions and occasional rule changes aimed at improving player safety, such as stricter enforcement of tackling techniques to minimize high tackles and the introduction of protocols to prevent players from returning too soon after a concussion.
Despite these measures, the risk of concussions in rugby remains a concern due to the physical nature of the sport. Continued efforts in education, research, and enforcing strict concussion protocols are crucial to mitigating the risks and ensuring the well-being of players at all levels of the game.